Air friction Damping: An air friction damping device is usually provided with moving iron instruments such as voltmeters and ammeters.
In this device, a light aluminum vane is attached to a spindle as shown in Fig.
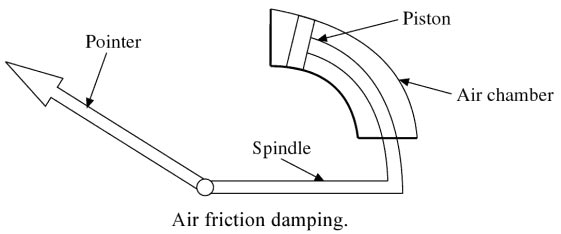
and this vane is free to move in a fixed air chamber known as a sector. When the pointer deflects, the vane in the sector also moves. The air in the sector produces friction in the movement of the vane and thus necessary damping torque is obtained.
Eddy Current Damping: It is used in a strong operating field e.g., PMMC (Permanent Magnet Moving Coil instrument) type.
Fluid Friction Damping: Used in high voltage measurement. Used in the vertically mounted instrument. e.g., Electrostatic type instrument.