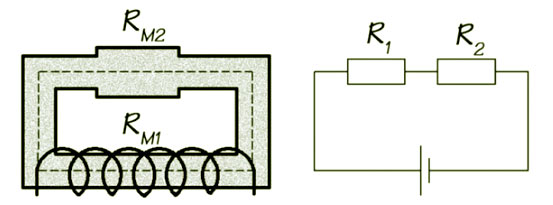
In the same way that we can have series, parallel or series-parallel electric circuits, we can also have equivalent series and series-parallel (but not parallel) magnetic circuits.
In practice, a magnetic circuit may consist of several parts in a series of different lengths, cross-sectional areas, and permeabilities. In such a series magnetic circuits, all the reluctances of several parts will get summed up together (as resistors in an electric circuit) to form the net reluctance of the circuit.
In series magnetic circuits the flux passing through each part will be the same (as current in the series electric circuits).